Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Serum PD-1 Levels Change with Immunotherapy Response but Do Not Predict Prognosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Hye Won Lee, Kyung Joo Cho, Soon Young Shin, Ha Yan Kim, Eun Ju Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):108-116. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.108
- 5,395 Views
- 151 Downloads
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
s: Programmed death receptor 1 (PD-1) is a promising new target for treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A high expression level of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a possible prognostic indicator for poor outcome in other malignancies. Here, we investigated the clinical significance of PD-1 and PD-L1 in patients with HCC.
Methods
We enrolled patients with HCC who underwent surgical resection at Severance Hospital between 2012 and 2017 and investigated the levels of PD-L1 in HCC tissues (tPD-L1) and PD-L1/PD-1 in serum (sPD-L1/sPD-1). We also aimed to determine whether expression levels correlated with clinical and histological features.
Results
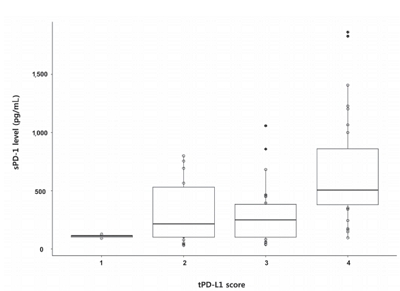
A total of 72 patient samples were analyzed. The median sPD-L1 and sPD-1 levels were 25.72 and 341.44 pg/mL, respectively. A positive correlation was detected between tPD-L1 and sPD-1 levels (R2=0.426, P<0.001). The median sPD-1 level increased linearly with tPD-L1 score (P=0.002). During the follow-up period, HCC recurred in eight (11.1%) patients and liverrelated mortality occurred in eight (11.1%) patients. Higher sPD-L1 levels (≥19.18 pg/mL) tended to be associated with liver-related mortality (hazard ratio 6.866; 95% confidence interval, 0.804-58.659, P=0.078). sPD-1 levels of patients treated with nivolumab as a second-line therapy changed serially, and a >50% reduction in sPD-1 levels was observed immediately after nivolumab administration. However, sPD-1 level was not associated directly with prognosis in patients with advanced HCC.
Conclusions
The results demonstrated that PD-L1 and PD-1 levels changed according to the immunotherapy. However, no significant association with clinical outcome in patients with HCC was detected. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Blood-based biomarkers for immune-based therapy in advanced HCC: Promising but a long way to go
Pil Soo Sung, Isaac Kise Lee, Pu Reun Roh, Min Woo Kang, Jaegyoon Ahn, Seung Kew Yoon
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum levels of soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1): A possible biomarker in predicting post-treatment outcomes in patients with early hepatocellular carcinoma
Tudor Mocan, Maria Ilies, Iuliana Nenu, Rares Craciun, Adelina Horhat, Ruxandra Susa, Iulia Minciuna, Ioana Rusu, Lavinia-Patricia Mocan, Andrada Seicean, Cristina Adela Iuga, Nadim Al Hajjar, Mihaela Sparchez, Daniel-Corneliu Leucuta, Zeno Sparchez
International Immunopharmacology.2021; 94: 107467. CrossRef - Interfacial interactions of SERS-active noble metal nanostructures with functional ligands for diagnostic analysis of protein cancer markers
Han-Jung Ryu, Won Kyu Lee, Yoon Hyuck Kim, Jae-Seung Lee
Microchimica Acta.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Status and Future Direction of Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What Do the Data Suggest?
Hye Won Lee, Kyung Joo Cho, Jun Yong Park
Immune Network.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Nivolumab for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Multiple Lung Metastases after Sorafenib Failure
Jaewoong Kim, Jin Won Chang, Jun Yong Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(1): 72. CrossRef
- Blood-based biomarkers for immune-based therapy in advanced HCC: Promising but a long way to go

- Subclassification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Intermediate Stage
- Hye Won Lee, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Snag Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Beom Kyung Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(1):17-22. Published online March 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.1.17
- 1,319 Views
- 13 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) intermediate stage includes a highly heterogeneous population. Here, we aimed to subclassify hepatocellular carcinoma with BCLC intermediate stage for better prognostification.
Methods
Between 2003 and 2008, 325 patients who were newly diagnosed as HCC with BCLC intermediate stage were considered eligible. Tumor factor and liver function were used for sub-classification. Overall survival (OS) was analyzed using Kaplan-Meier method with a comparison by log-rank test.
Results
A total of 325 patients with intermediate stage HCC were analyzed. Patients with tumor size ≥7 cm, tumor number ≥4 and Child-Pugh class B had the worse OS compared to those with tumor size <7 cm, tumor number <4 and Child-pugh class A, respectively (all P<0.05). These three variables affected the OS independently from multivariate Cox regression analysis (all P<0.05). So, using these three variables, patients were finally sub-classified as those with fulfilling none of three factors (B-a), one of three factors (B-b), two of three factors (B-c) and all of three factors (B-d) with the median OS of 39.2, 20.6, 12.0 and 8.3 months with statistical significances (all P<0.05 between B-a and B-b, between B-b and B-c, and between B-c and B-d), respectively.
Conclusions
Sub-classification of HCC with BCLC intermediate stage may be useful in not only prognostification but also guidance of treatment strategies. (J Liver Cancer 2016;16:17-22)

Case Report
- A Case of Rapidly Recurred Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Distant Metastasis after Surgical Resection
- Mi Yeon Kim, Hye Won Lee, Kyu Sik Jung, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2015;15(2):136-139. Published online September 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.15.2.139
- 897 Views
- 7 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the cancers with poor prognosis. However, surgical resection is the treatment of choice as curative aim for early HCC with preserved liver function. A 5 year survival rate after curative resection is over 50%. We experienced a case of rapidly recurred HCC with bone metastasis after surgical resection. In our case, microscopically microvessel invasion was present after resection. Microvascular invasion (MVI) is an important factor to influence survival and/or HCC recurrence. So we suggested the patients with MVI need to follow up intensively and adjuvant therapy may be considered.

Original Article
- Characteristics and Survival of Korean Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Nationwide Random Sample Study
- Young-Suk Lim, Seung Hyung Kim, Seung Hyung Kim, Jae Seok Hwang, Kwang-Hyub Han
- J Liver Cancer. 2014;14(2):97-107. Published online September 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.14.2.97
- 1,295 Views
- 27 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Given the high incidence and mortality rate of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), ensuring high quality of registry data is important for the improvement of health service. Registries by voluntary reporting often lack case completeness and may cause selection bias. A statutory Korean Central Cancer Registry (KCCR) has case completeness and provides accurate information on HCC incidence, but provides limited information about HCC characteristics.
Methods
The Korean Liver Cancer Study Group (KLCSG) and the KCCR jointly built a nationwide cohort of patients who were diagnosed with HCC between 2003 and 2005. Out of 31,521 new HCC cases that were registered at the KCCR between 2003 and 2005, 4,630
case
s (14.7% of total HCC cases) were randomly selected and abstracted from 32 hospitals nationwide, and followed up until December 2011. After excluding 110 patients who met the exclusion criteria, a total of 4,520 HCC patients were analyzed.
Results
Mean age at the diagnosis of HCC was 57.1±10.8 years, and males comprised 81.0%. Hepatitis B was the predominant etiology (72%), and hepatitis C comprised 12%. Stage at diagnosis was 10%, 43%, 28%, 11% and 8% for modified International Union Against Cancer (mUICC) stages I, II, III, IV-A and IV-B, respectively. Initial treatment modalities were transarterial therapy in 53%, surgical resection in 10%, local ablation in 7%, and liver transplantation in 1%. The median survival was 1.4 years, and the 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates were 56%, 35% and 27%, respectively. Age, gender, Child-Pugh class, etiology, tumor stage at diagnosis, and treatment modality were factors independently related to survival.
Conclusions
About half of HCC patients are diagnosed at advanced stages in Korea. Curativeintent treatments are rarely applied to patients. This data provides unbiased information about the characteristics and outcome of HCC patients in Korea. (J Liver Cancer 2014;14:97- 107) -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Young Eun Chon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Sik Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(2): 135. CrossRef - Subclassification of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer B and C hepatocellular carcinoma: A cohort study of the multicenter registry database
Sangheun Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Kijun Song, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Seung Up Kim, Kwang‐Hyub Han, Do Young Kim
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2016; 31(4): 842. CrossRef
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry

Case Reports
- A Case of Positive Tumor Marker Response after Intra-arterial Deferoxamine Infusion Therapy in a Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patient with Decompensated Liver Function
- Hyun Ju Kim, Wonseok Kang, Mi Na Kim, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han
- J Liver Cancer. 2014;14(2):127-130. Published online September 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.14.2.127
- 1,127 Views
- 6 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma is often very challenging when the underlying liver function is decompensated. Recent experimental and clinical studies showed that some chelating agents, including deferoxamine, display anti-proliferative actions against tumor cells, thereby exhibiting anti-cancer effect in certain cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Based on previous studies, we herein offer our experience of positive tumor marker response after intra-arterial deferoxamine infusion in a patient presenting with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with decompensated hepatic function. Validation of the efficacy of intra-arterial deferoxamine therapy in the setting of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with underlying decompensated hepatic function is warranted. (J Liver Cancer 2014;14:127-130)

- A Case of Partial Response of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Induced by Concurrent Chemoradiation and Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy after Trans-Arterial Chemoembolization
- Myung Eun Song, Sangheun Lee, Mi Na Kim, Dong-Jun Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Chae Yoon Chon, Kwang-Hyub Han, Jinsil Seong, Do Young Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2013;13(2):152-157. Published online September 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.13.2.152
- 953 Views
- 7 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 63-year-old man patient was referred for treatment of infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with hilar invasion after transarterial chemoembolization. Serum alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin were elevated, liver dynamic CT showed infiltrative type mass in left hepatic lobe and right hepatic dome with hilar invasion and left intrahepatic duct dilatation. Also CT showed obliteration of left portal vein and metastasis of lymph node around common bile duct. He was diagnosed as hepatocellular carcinoma (UICC stage IV-A, BCLC stage C). With the percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage and the concurrent chemoradiation therapy and the 4th cycle of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for infiltrative mass, viable tumor was decreased in resectable size at eight months from initial diagnosis.

- A Case of Recurred Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Treated by Trans-Arterial Chemoembolization
- Sangheun Lee, Mi Na Kim, Young Eun Chon, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Chae Yoon Chon, Kwang-Hyub Han
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2013;13(1):74-79. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.13.1.74
- 1,060 Views
- 4 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocelluar carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver cancer in the world and the most prevalent cancer among patients liver cirrhosis. The management of HCC depends on tumor stage and the degree of liver dysfunction. Patients with intermediate-stage HCC are ineligible for surgical or local ablative treatments. Current treatment guidelines recommend trans-arterial chemoembolization (TACE) for intermediate stage of HCC. However, tumor recurrence after TACE is universal and the survival benefit is relatively small. Hence, new strategies are needed to improve the outcome of HCC patients undergoing TACE. Recently, the combination of target agents with TACE has shown promising overall survival in advanced HCC. It is necessary to investigate new treat strategy how to increase treatment outcome of advanced HCC by new treat strategy.

- A Case of Necrotizing Pancreatitis after Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Mi Na Kim, Jung Hyun Cho, Young Eun Chon, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Chae Yoon Chon
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(2):155-159. Published online September 30, 2012
- 557 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Acute pancreatitis is a rare but severe postprocedural complication after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) of hepatocellular carcinoma with an incidence of 1.7-4%. The proposed mechanism of this complication is inadvertent embolization through collateral vessels or regurgitation of chemotherapeutic agents to the arteries of other organs. Here, we present a fatal necrotizing pancreatitis case which developed 10 days after TACE, caused by the regurgitation of the chemotherapeutic agents to the pancreas during the procedure. The patient recovered with conservative care at first, but after suffering from several times of recurrent pancreatitis, he died of peritoneal septic shock 5 months after the initial pancreatitis attack.

- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurred Extensively during Treatment of Biliary Complication Occurring after Transarterial Chemoembolization
- Hyun Jung Oh, Hana Park, Kwang Hoon Lee, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Chae Yoon Chon, Jun Yong Park
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2011;11(2):178-184. Published online September 30, 2011
- 522 Views
- 3 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC) is one of the cancers with poor prognosis. Transarterial chemoembolization(TACE) has been widely used for treating unresectable HCC. Although TACE is considered as a less invasive and relative safe procedure, severe complications such as hepatic failure, pulmonary embolism, liver abscess, biloma formationcan occur rarely after TACE. These complications sometimes may lead to fatal clinical situation, even death. We reported a case of HCC recurred extensively during treatment of biliary complication after TACE. A 44-year-old male with HCC was admitted due to fever for 3 days after undergoing TACE. Three weeks before the admission, he had been diagnosed with HCC recurrence which presented as two arterial enhancing nodules in MRI and treated with TACE. CT scan showed 7 cm sized air containing fluid collections with necrosis suggestive of liver abscess and 15 cm sized biloma formation. Because the patient was in septic shock at admission, percutaneous catheter drainage was performed with use of broad spectrum antibiotics. After treatment of 3 months, the sizes of hepatic abscess and biloma were remarkably decreased. However, 1 month later, large size tumor recurrence and perihepatic lymph node metastasis were found on a follow-up CT scan. In this case, the cause of rapid growing recurrence after TACE is uncertain, but the development of unanticipated complication seems to affect the progression to poor prognosis. Therefore, early recognization of predisposing factors with proper management would be needed to prevent these serious complications after TACE.

- A Case of Early Recurred Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Initial Expectation of Good outcome by Surgical Resection
- Jung Min Lee, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Kyung Sik Kim, Young Nyun Park, Myeong-Jin Kim, Chae Yoon Chon, Kwang-Hyub Han
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):41-44. Published online June 30, 2009
- 542 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the cancers with poor prognosis as HCC develops on base of cirrhosis in majority cases, which requires multidisciplinary approach. If feasible, however, surgical resection is the choice of treatment, and many previous studies and guidelines offered appropriate indications for surgical resection; firstly, preservation of liver function should be confirmed with traditional Child-Pugh classification or more recently with Indocyanine Green retention test or absence of portal hypertension. Secondly, several variables about the size, number, and vascular invasion of tumor should be taken into consideration. It is suggested that to lessen the risk of recurrence gross vascular invasion be absent and the number of tumor be single. Regarding the size of tumor, although risk of dissemination increases with size, some tumors may grow as a single mass and thus the size of tumor is not a clear-cut limiting factor. Based on above suggestions, we herein offer our experience of a patient with initial hopeful expectation of good outcome with surgical resection, but who eventually turned out to result in disseminated tumor recurrence. Further study, maybe regarding a combination of adjuvant or neoadjuvant transarterial chemoembolization/chemotherapy or radiotherapy, is necessary on how to manage such patient.

- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Young Age Younger than 20 Years Old
- Joo Won Chung, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Chae Yoon Chon, Geung-kyu Ko, Jin Sil Seong, Jong Hee Chang, Do Young Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):71-75. Published online June 30, 2009
- 487 Views
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is very rare in young age. Most young patients tend to receive the evaluation only when they experience intractable or persistent symptoms. Therefore, HCC in young patients is often diagnosed at advanced stage and thus, young HCC patients have a worse prognosis than older HCC. However, because young HCC patients show well-preserved liver function than older HCC, they are tolerable to more aggressive treatments. We report a case of advanced HCC in 13-year and 8-month old male who has been a B-viral carrier. Despite the tumor size decreased after concurrent chemoradiation therapy, multiple lung and brain metastases developed. He underwent radiofrequency ablations on lung metastases and gamma-knife surgery on brain metastasis, and he has received systemic and intra-arterial chemotherapy. The screening and early diagnosis of HCC in young age is needed especially for B-viral carrier with a family history of HCC.

- A Case of Localized Concurrent Chemo-radiation Therapy Using with Tomotherapy for Hilar Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Invasion of Bilateral Bile Duct
- Ki Tae Yoon, Do Young Kim, Jin Sil Seong, Jun Yong Park, Jong Won Choi, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Chae Yoon Chon
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2008;8(1):102-105. Published online June 30, 2008
- 456 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) usually takes an intrahepatic spread via portal vein branches, and the incidence of portal vein invasion is reported to be 34~40% in surgical resected series. On the other hand, the rate of intrabiliary growth of HCC is rare, ranging from 2.3~13% in surgical and autopsy cases. Here, we report a case of the patient treated with localized concurrent chemo-radiation therapy (CCRT) for hilar HCC with invasion of bilateral bile duct. The tomotherapy was performed with a total radiation dose of 4,240 cGy (20 times, 212 cGy/time) on tumor bed and hepatic arterial infusion of 5-fluorouracil (1,000 mg/day, day 1~5 and day 16~20) and cisplatin (60 mg/m2, day 3 and day 18) was done via implantable port system during the radiotherapy. After that, tumor size and tumor marker was decreased and treatment response was achieved as partial response. CCRT is expected as one of the appropriated treatment options for inoperable HCC with bile duct invasion.

- A Case of Focal Nodular Hyperplasia-like Nodules in Cirrhosis
- Young Joon Yoon, Ki Tae Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Hyun Woong Lee, Hwa Sook Kim, Jae Kyung Kim, Young Nyun Park, Kwang-Hyub Han, Chae Yoon Chon, Young Myung Moon, Mi-Suk Park, Sang Hoon Ahn
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2007;7(1):41-44. Published online June 30, 2007
- 725 Views
- 38 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) usually occurs in non-cirrhotic livers and was defined as a nodule composed of benign appearing hepatocytes occurring in a liver that is otherwise histologically normal or nearly normal. However, due to improvements in imaging techniques and pathological evaluation of explant livers, a focal lesion that is very similar to the classic form of focal nodular hyperplasia that occurs in cirrhotic liver has been described by several reports. Therefore, the term FNH-like nodules has been proposed. In this report, we report a case of focal nodular hyperplasia-like nodules in cirrhosis. A 59 year old woman with known hepatitis B virus infection visited our institution for routine check up. She was diagnosed as having liver cirrhosis and 3.5 cm sized liver mass on abdomen ultrasonography (US). Because tumor marker was negative and US findings are not compatible with hepatocellular carcinoma, other imaging modalities were performed. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) documented a 3.5 cm sized hypervascular nodule with internal aberrant vascular structure and multiple small sized nodules in remaining liver. Needle biopsy was targeted to the liver main mass. Microscopic finding revealed FNH-like nodule and underlying liver cirrhosis.

- Two cases of Vessel invasion of Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Sae Byeol Choi, Jae Yeon Seok, Kyung Sik Kim, Young Nyun Park, Kwang-Hyub Han, Jong Tae Lee
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2007;7(1):71-76. Published online June 30, 2007
- 527 Views
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Despite growing information on the clinical behavior of hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC), the histologic features associated with survival are not well characterized. Several different staging systems are suggested for use in predicting the prognosis of HCC. American Joint Committee on Cancer/International Union Against Cancer Staging System (AJCC/UICC) 6th edition divided T stages according to vessel invasion, T1 without microvessel invasion, T2 showing microvessel invasion and T3 showing major vessel invasion. The vessel invasion is generally considered a poor prognostic factor for HCC. Our report of the two patients with HCC run along similar terms. The patient diagnosed HCC with microvessel invasion underwent left lateral sectionectomy. Although the presence of microvessel invasion was found, this patient has survived without any recurrence for over 5 years now. The other patient underwent S8 segmentectomy and lived 10 years disease-free. After 10 years, although an intrahepatic recurred HCC successfully treated with local therapy, the recurred and newly developed multiple lesions were found again leading to a decision to perform operation. The HCC invaded into the portal vein and constituted portal vein thrombosis. The patient expired after 3 months postoperatively due to intrahepatic dissemination of the tumor. Therefore the impact of the vascular invasion on long-term survivors remains to be determined.

- Excellent Response to Hepatic Arterial Infusional Chemotherapy in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis
- Keun-Ho Lee, Ja Kyung Kim, Kwang-Hyub Han, Jong Tae Lee, Do Youn Lee, Jong Yoon Won, Hyun Woong Lee, Hwa Sook Kim, Ki Tae Yoon, Sang Hoon Ahn, Chae Yoon Chon, Young Myoung Moon
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2006;6(1):42-46. Published online June 30, 2006
- 527 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There is no treatment of curative aim in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein thrombosis (PVT), which is associated with poor prognosis. Albeit one of the treatment options is intra-arterial infusional chemotherapy, its therapeutic efficacy was minimal. In this report, we present an unusual case of a patient with favorable result after intra-arterial infusional chemotherapy. This patient was HBV carrier and diagnosed having HCC of stage IVb (T4N0M1) with right PVT on February 1999. Direct right adrenal gland and right kidney invasion and numerous intrahepatic metastases were also noted. The serum AFP level showed more than 60,000 ng/mL, and the Child-Pugh score was 5 (class A). The patient received three sessions of intra-arterial 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and cisplatin combination chemotherapy and two additional sessions of systemic (5-FU) chemotherapy combined with intra-arterial cisplatin infusion. After total 5 sessions of combination chemotherapy, follow-up CT scan revealed grossly total necrosis of main HCC and numerous intrahepatic metastases, without evidence of viable portion in July 1999. The AFP level decreased to 79.4 ng/mL. The latest CT scan taken in November 2005 also showed no evidence of recurrence. It is noteworthy that the patient with advanced HCC with PVT showed complete remission only after 5 sessions of intra-arterial chemotherapy and the status of complete remission is maintained for more than 76 months.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter